AWS Migration from On Premise to Aws cloud

Steps:
Preparation
Planning
Migrate
Monitor
Optimize
7 R`s- AWS Cloud Migration Strategies
Rehost mechanism - Basically lift &shift strategy. Moving the services from on prem(private cloud) to Aws cloud (public cloud)with same os types and independent of h/w, platform independent. Eg:vpshere to aws
Replatform mechanism- Here once you move from on prem to aws cloud, you take advantage of aws platform services eg: containerisation, scalablity, HA.
Refactor/Rearchitecture model - Suitable in monolithic application when migrated, we have to rearchitecture your application to move into microservices, so you will choose best approach eg: security, scalability and HA.Repurchase - Very less used these days. Lets say you use vmware on premises, when you move into aws or you look for same kind of platform.
Relocate - Consider you have K8 cluster running on prem. You will move to EKS or openshift on AWS (popularly called as ROSA). It is costly and you are changing the platform as well. So need to be extra cautious while using this strategy.
Retire - Out of 100 applications, you see 10 application no user is using them. So you retire them rather than migrating.
Retain - Consider some services or application which you have and they are secured and the organisation doesn’t want to migrate that to aws. Other services will be henceforth migrated to aws and there will be a secure gateway to connect them over on prem. This type of strategy is called as Retain mechanism.
Preparation & Planning (One time activity)--It is a part of cloud migration strategy. Consider a example with an organization with 200 microservices and single monolithic application.
Now organization wants the monolithic application transform to microservice architecture. This is the preparation stage and you will consider the current architecture of your application. When you want the application to move into cloud native nature, we look out for microservices especially containers or orchestration platform.
While in the planning stage, you will decide:
-- which services have to go into beginning phases. That is splitting 200 services into 5 phases. Eg: phases can be 1,2….
So the critical ones will be at the last stage eg: phase 5
the less critical ones will be at the beginning phase eg: phase 1
Migration & Monitor-- Migration can be in multiple phases. Migrate phase may have TF scripts for creating ec2 instances or cron jobs or cloudwatch logs. Once the migration is done and you will monitor the application for a while depending on the criticality. Testing team may create testautomation script to run once in a day as an example. So we can create a dashboard or check the performance on the monitoring tool to review them.
Optimize -- Once the migration is done, we evaluate what did we achieve ? -- cost benefit, overall maintenance cost is lowered, performance improvement has happened post migration. If the cost optimization is 40 % , can we optimize to 50% and we can create JIRA or task for improvement.
When your applications are linked to databases
-Take backup of databases
-Find a right fit that is using aws RDS eg from mssql to Nosql
- Incase of any uncalled situation, you will simply point the databases to the on prem environment.
How to configure the MGN (Application Migration service) and setting up the templates (Replication, Launch template..) in AWS console.

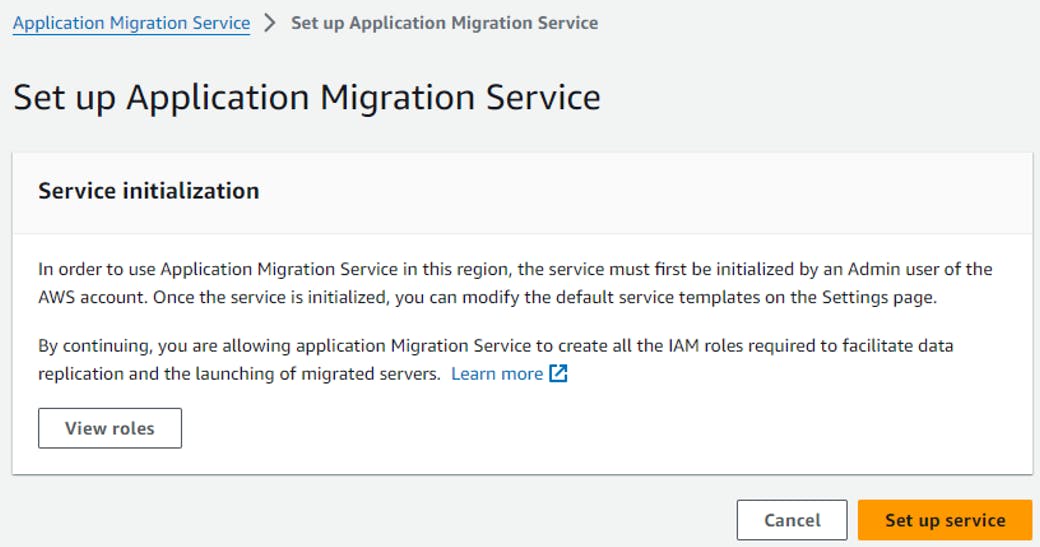
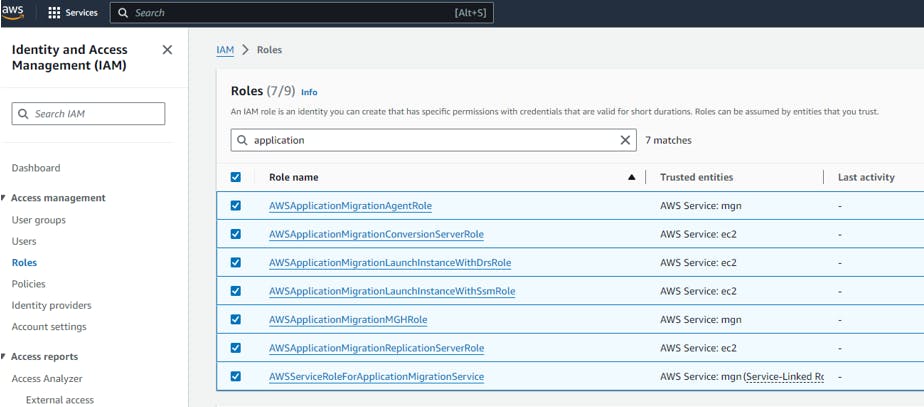
Once you initialize MGN, there are 7 roles created.
You will see 3 templates here:
Replication Template
Launch Template
Post launch Template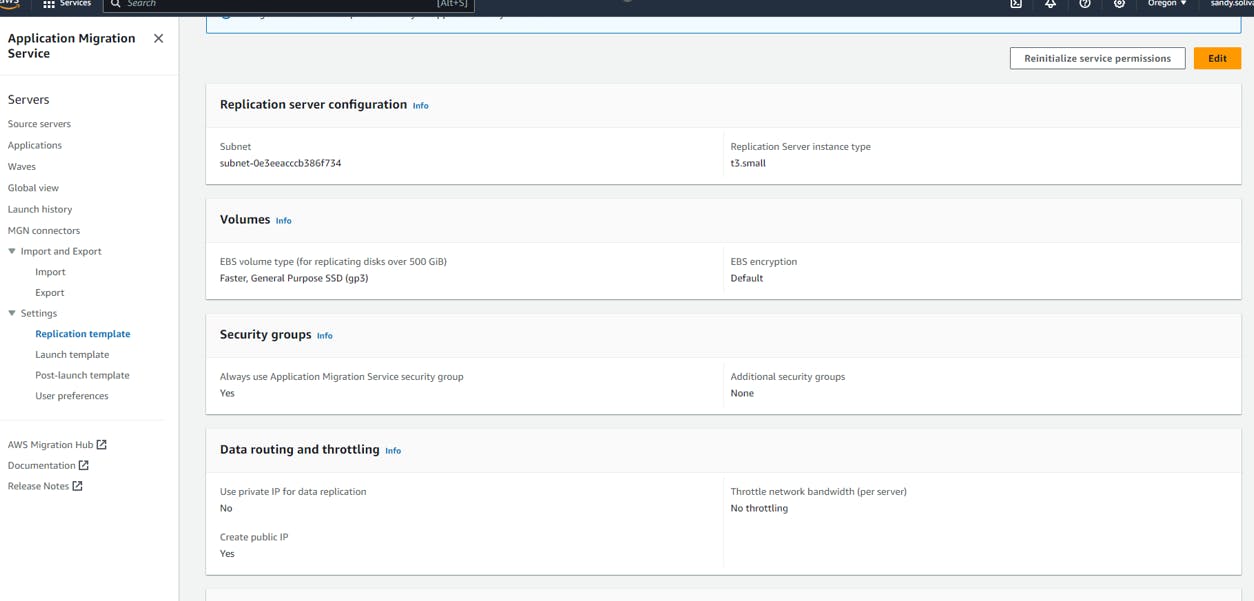
So you may edit the parameters here in the templates based on your requirement as in ec2 instance type, EBS volume type as in gp3 or gp2.
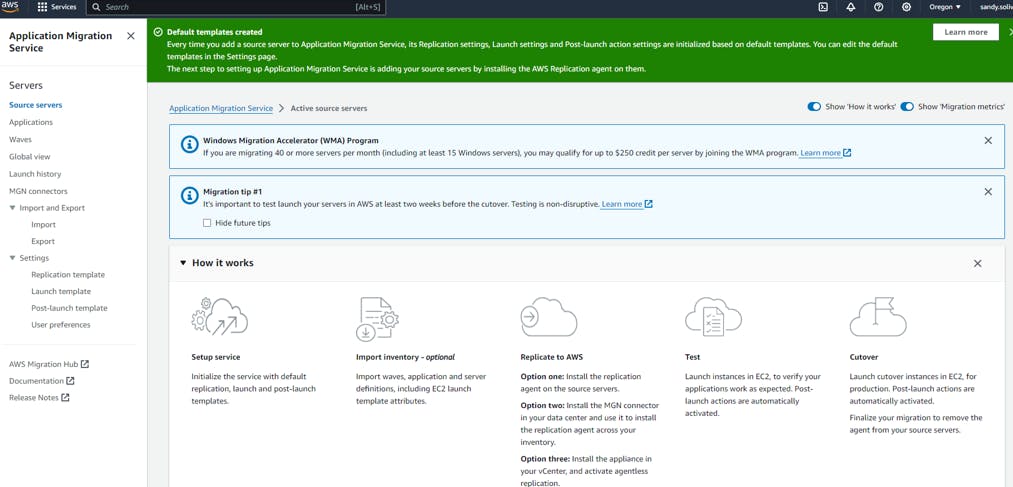
-You may follow the below article for installing aws replication agent onto your on premises box(depending on the OS)
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/drs/latest/userguide/agent-installation.html
Next step create a User(MGNuser) in IAM (with least privilege) as service account
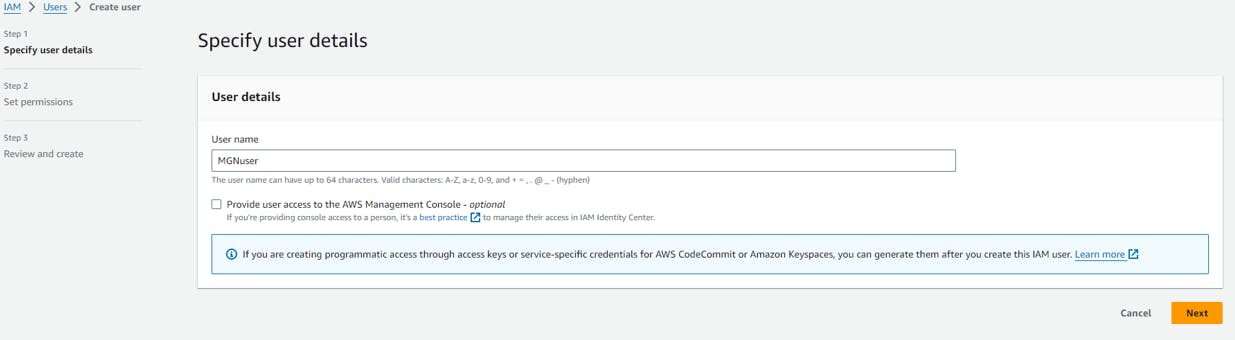
Now set policy to AWSApplicationMigrationAgentPolicy as below

Create the access key here:
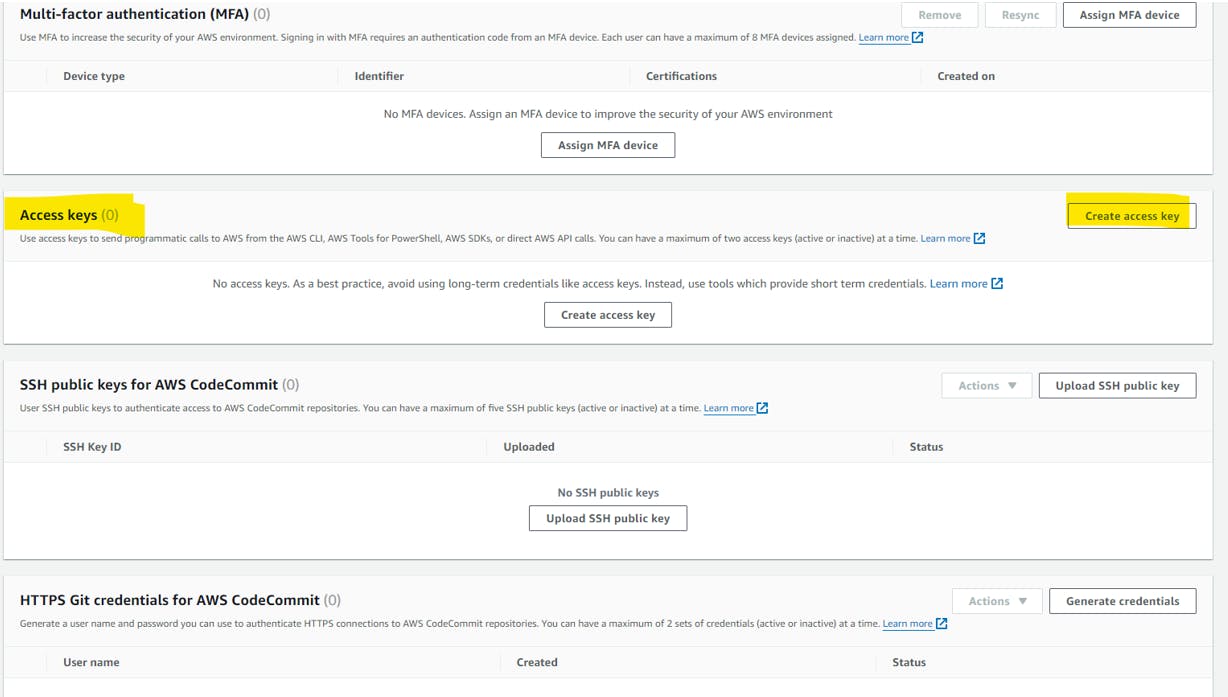
Once the above process are completed and the servers have been configured with replication agent.
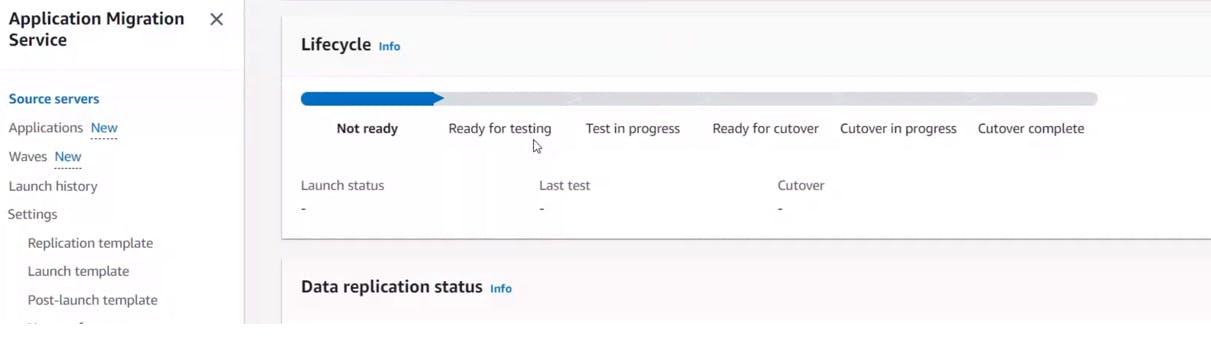
Here you will find the below parameters:
1- Replication progress2-Elapsed replication time
3-Total replicated storage
4-Replication type – Agent bases or Agentless
From here we can have POC(proof of concepts), decides how much downtime we need to set for the entire process of migration.
POC is determined by time taken during pilot migration , N/w bandwidth etc.
As stated above: we have 6 stages or lifecycles:
1-Not Ready- The server is undergoing sync process and is not ready for testing.
2-Ready for Testing-The server has been successfully added to MGN (Application migration service). Sync is done.
3-Test in progress – The test instance is embarked currently.
4-Ready for cutover-The server has been reviewed and tested and is ready for the cutover to begin.
5-Cutover in progress – A cutover instance is launched currently.
6-Cutover complete-The cutover has completed and all the data of this server has been migrated to the new launched cutover instance.
Under source server-check for test and cutover
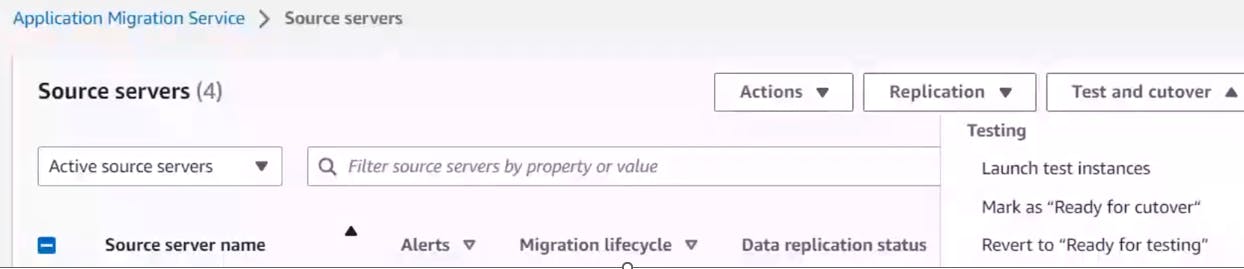
Only when the launch test instance and mark as ready for cutover is done, we will be able to launch the cutover as below.
Summary of all the steps:
1- Initialising the MGN and setting up roles in IAM
2- Create a IAM service account with privileges (AWSApplicationMigrationAgentPolicy)
3- Do a system review from past using tools like New relic etc.
4- Installing the replication agent on the on Prem servers which will undergo migration.
5- Review the replication status
6- Review the launch template and then launch the test instance.
7- Verify the health of test instances
8- Mark ready for cutover
9- Power down source server
10- Launch cutover instance.
11- Review the cutover instance.
12- Perform the application related copying and configuration based on your organisation and validate them as well.
13- Check for the DNS update and under route53 test the record.
14- Test application
15- Finalize cutover
16- Mark as archived
17- Check in fleet manager if there are connecion lost status of ssm agents and duplicated instances.